Mapping
Product positioning mapping can be called brand positioning mapping or simply perceptual mapping. These terms are used interchangeably to describe the same technique of visually mapping the perceptions of consumers regarding brands or products.
The purpose is to understand how consumers perceive and position different brands or products in the market based on specific attributes. It is a tool that helps businesses gain insights into consumer perceptions, preferences, and the competitive landscape. Perceptual mapping is a technique used in marketing to visually represent how consumers perceive and position products or brands in relation to each other based on specific attributes. One common approach is to use a two-dimensional graph, with the x-axis representing one attribute and the y-axis representing another.
Mapping can be linked to the STP process, specifically to the positioning stage. After segmenting the target market and selecting the target segments, businesses need to determine how they want their brand or product to be positioned in the minds of consumers within those segments. Perceptual mapping helps in this process by providing a visual representation of the current market positioning, allowing businesses to identify gaps or opportunities for differentiation.
By analyzing perceptual maps, businesses can assess the positioning of their own brand relative to competitors and make informed decisions about how to position themselves more effectively. They can identify unique positioning opportunities, understand consumer perceptions of different attributes, and develop strategies to position their brand as distinct and desirable to the target market segments.
This picture illustrates an example of the mapping process for MonChlo that focuses on quality and material. Material is represented on the x-axis, and quality is on the y-axis.
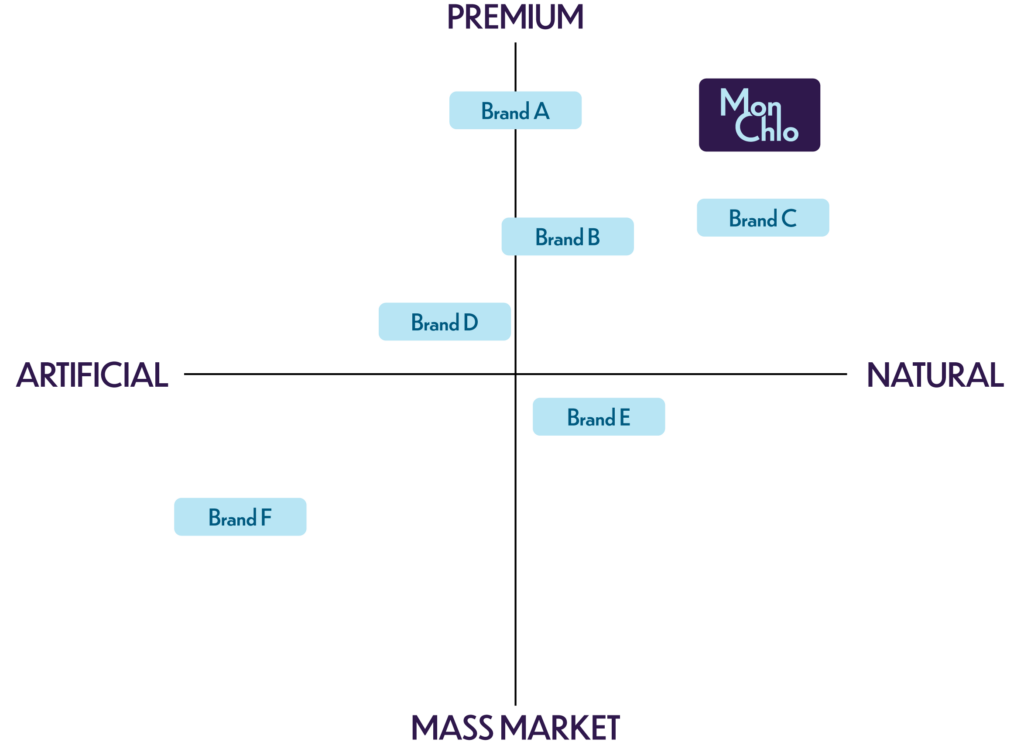
Using the graph above, the positioning of different brands (A, B, C, D, E and F) is based on consumer perception in terms of material and quality. Products that are perceived as natural and high quality are positioned in the top-right quadrant of the perceptual map (Brand C). On the other hand, brands that are perceived as made of artificial material and low-quality (mass market) may be positioned in the bottom-left quadrant (Brand F). Brands that utilize natural materials but are mass marketed are found in the bottom-right quadrant (Brand E). Products that are perceived as made of artificial material and high quality are positioned in the top-left quadrant of the perceptual map (Brand D). Products that are made of both natural and artificial material can be positioned on the y-axis, but as they are perceived as premium are on the top half of the graph (Brand A and B). Looking at the graph, Brand A is viewed as more premium than all other brands. MonChlo is perceived by customers as very premium and very natural.
The positioning of products or brands on the perceptual map allows marketers to gain insights into consumer perceptions and identify opportunities for differentiation. It helps in understanding how customers perceive the relationship between quality and price and can guide marketing strategies, such as pricing adjustments or quality enhancements, to better align with target market preferences. By analyzing the perceptual map, marketers can identify gaps in the market, uncover unmet customer needs, and make informed decisions on product positioning, pricing strategies, and overall marketing efforts. Perceptual mapping is a valuable tool for market research and strategic planning, providing valuable insights into consumer perceptions and competitive positioning.
In summary, perceptual mapping is a valuable tool within the STP process as it helps businesses understand consumer perceptions and strategically position their brand or product in the market.