Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive framework for measuring and managing the performance of an organization. It goes beyond financial metrics and incorporates a balanced set of performance indicators across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
The Balanced Scorecard recognizes that financial performance alone is not sufficient to evaluate the overall health and success of an organization. By incorporating multiple perspectives, it provides a more holistic view and helps align the organization’s strategic objectives with its operational activities.
Here’s a brief overview of each perspective and its connection to strategic operations:
- Financial Perspective:
- This perspective focuses on financial indicators such as revenue, profitability, return on investment, and cash flow.
- It helps organizations monitor their financial performance and evaluate the effectiveness of their operational strategies in generating financial results.
- Customer Perspective:
- The customer perspective looks at measures related to customer satisfaction, loyalty, market share, and customer retention.
- It helps organizations assess their ability to meet customer expectations and deliver value through their products, services, and customer relationships.
- Internal Processes Perspective:
- This perspective examines the operational processes and activities that drive value creation, efficiency, and quality within the organization.
- It identifies key internal processes and sets performance indicators to monitor and improve their effectiveness, such as production cycle time, defect rates, or process efficiency.
- Learning and Growth Perspective:
- The learning and growth perspective focuses on the organization’s ability to develop and leverage its intangible assets, including employee skills, knowledge, innovation, and infrastructure.
- It highlights the importance of continuous learning, employee development, and creating a supportive culture to drive innovation and adaptability.
The connection between the Balanced Scorecard and strategic operations lies in its ability to translate strategic objectives into actionable measures and targets. By aligning the operational activities and performance metrics across the four perspectives, organizations can ensure that their daily operations contribute to the achievement of their strategic goals.

In summary, the Balanced Scorecard is a valuable tool in strategic operations management as it provides a framework for measuring, monitoring, and managing performance across multiple perspectives, ensuring that operational activities are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
To provide further insight, let’s delve into a case study that demonstrates the practical implementation of the Balanced Scorecard within MonChlo, our fictional technology company. This case study exemplifies how MonChlo effectively utilizes the Balanced Scorecard to drive strategic decision-making and achieve its organizational goals.
MonChlo Balanced Scorecard Case Study
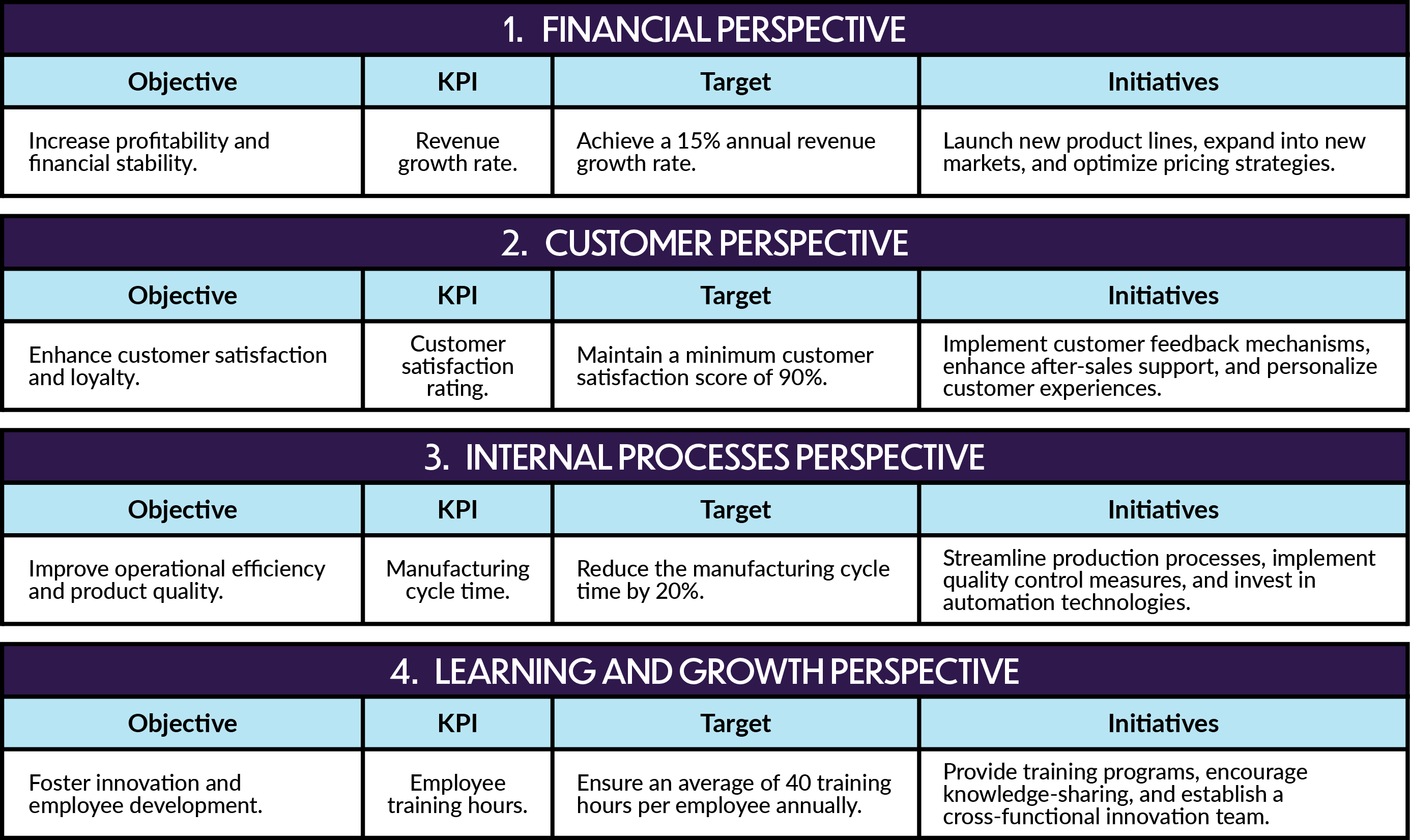
With the Balanced Scorecard in use, MonChlo can monitor and measure its performance against the established objectives and targets across the four perspectives. The scorecard enables a holistic view of the company’s strategic progress and ensures that operational activities align with the overall strategy.
For example:

Regular review of the Balanced Scorecard allows MonChlo to identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions. If performance falls short of targets, appropriate actions can be taken to address the gaps and realign operational activities. By adopting the Balanced Scorecard approach, MonChlo can enhance its strategic operations management and drive long-term success.